Car Insurance Value Chain
This also shows a selection of the newcomers claiming their share in the traditional value chain and uproot the traditional value proposition of insurers.
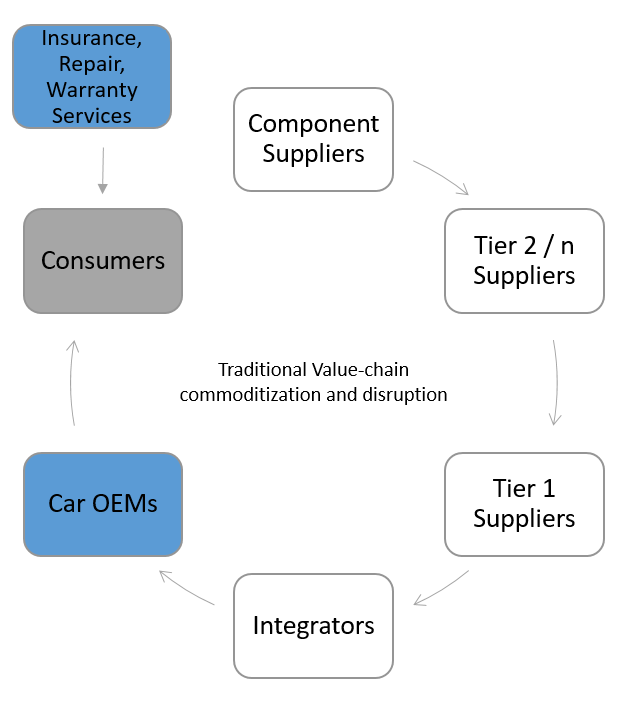
Car insurance value chain. At the customer interfaces across the insurance value chain. The supply chain represents all the steps required to get the. Customers and the claims value chain. There many links in the health insurance value chain and all of them play a part in the amount that health care costs individuals and businesses.
Unbundling of the value chain. P oo r re s pon se unplanned ev en t number of high intensity braking events at high speed per kilometer. The value chain is a process in which a company adds value to its raw materials to produce products eventually sold to consumers. Advances in software and hardware are transforming big data into actionable insights as the insurance industry reaps productivity gains from the most recent wave of automation new technologies are significantly enhancing operational.
Although these newcomers are populating every part of the value chain exhibit 2 their focus to date has been on the more easily accessible slivers of the industrymainly distribution particularly in property and casualty insurance. The links of the chain are interconnected and cost increases in one link will usually affect the other links of the value chain as well. Simply put the traditional insurance value chain can be dissected into various activities as seen in figure 1. The value added services landscape in insurance a combination of supply and demand forces has given.
A value chain is a series of activities or processes that aims at creating and adding value to an article at every step during the production process. This in turn is fueling greater competition in the industry leading to further emphasis on a customer centric approach that can differentiate the firm in a competitive market. Value is realized across the value chain with customers benefiting from more accurate insurance quotes emergency breakdown support when needed and in the case of an accident a faster settlement. As a type of distributed ledger a blockchain can store data derived from a number of disparate sources more securely and efficiently than a centralized database.
Several insurance consortiums have formed in recent years to develop blockchains for use in the insurance industry and while the technology is still young its uses look promising.